Welcome
to Johnbirchall-economist.com!
(The single
currency (Euro))
The
history of the Single Currency
EMU
STORY
The idea of an economic and monetary
union in Europe started well before the Treaties establishing the European
Communities after the Second World War (for example, already in the League
of Nations, Gustav Stresemann asked in 1929 for a European currency
against the background of an increased economic division due to a number
of new nation states in Europe after the Treaty of Versailles. (Historical
documentation of EMU)
How
the Euro evolved
Part 1: 1960 - 1969
The run-up to the Barre Plan
Part 2: 1969 - 1971
The first plans by stages to create an economic and monetary union
Part 3: 1971 - 1975
From the floating US-Dollar to the European Monetary System
Part 4: 1975 - 1980
The need to coordinate economic policies
Part 5: 1980 - 1988
The ECU in the centre of discussion
Part 6: 1988 - 1991
The run-up to the Maastricht Treaty
Part 7: 1992 - 1993
Work within the first phase of EMU
Part 8: 1994 - 1998
Work within the second phase of EMU
Part 9: 1999 - 2000
The start of the euro area ("EUR11")
Part 10: 2001 - 2002
The realisation of the third phase and enlargement of the euro area
("EUR12")
Other
Resources
http://ec.europa.eu/economy_finance/emu_history/documents/Presentations/
A%20single%20currency%20for%20Europe.ppt#1
An excellent power point presentation on
the reasons for the Euro and its role in EU expansion
http://ec.europa.eu/economy_finance/emu_history/documents/Presentations/
The%20Euro%20and%20international%20aspects.ppt#13
An excellent power point presentation on
the Euro and its international implications
http://www.ecb.eu/home/html/index.en.html
- The European Central Bank
Introducing
the Euro
Economic and monetary union (EMU)
comprises various stages.
The main objective of Stage
One, which began in 1990, was the complete liberalisation of capital
movements under Article 56 of the EC Treaty.
In Stage
Two, which began on 1 January 1994, the Member States implemented
measures enabling them to achieve the convergence targets necessary in
order to enter Stage Three of EMU and guaranteed the independence of their
central banks. The process of coordinating economic policies and ensuring
multilateral surveillance of progress with convergence began in the course
of Stage Two. The Member States were called on to do all they could to
avoid excessive public deficits.
In Stage Two the Member States had to
take measures to free their central banks of political interference.
Central banks are now responsible for monetary policy and, as such,
determine interest rates in the euro zone. They were also prohibited from
financing a budget deficit affecting the European institutions, the
governments of the Member States or other authorities, be they regional or
local, and from granting loans to state-owned companies.
Stage
Three of EMU began on 1 January 1999 with the launch of the euro on
financial markets. Under the accession treaty, the new Member States went
straight into Stage Three of EMU on 1 May 2004.
What
you must show before entering the Euro Zone
-
Price
stability, measured according to the rate of inflation in the
three best performing Member States;
-
Long-term
interest rates close to the rates in the countries with the best
inflation results;
-
An
annual budget deficit which does not exceed 3% of gross domestic
product (GDP) and total
government debt which does not exceed 60% of GDP or which is
falling steadily towards that figure;
-
Stability
in the exchange rate of the national currency on exchange markets
The exchange-rate mechanism of the European Monetary System requires
this stability to be demonstrated and sustained for two years.
Some
of the important data to consider when analysing the Euro and those who
wish to join
New Member
States Budget Deficits
|
New members
|
2000
|
2001
|
2002
|
2003
|
2004
|
2005
|
|
Cyprus
|
-2.4
|
-2.4
|
-4.6
|
-6.3
|
-4.6
|
-4.1
|
|
Estonia
|
-0.3
|
0.3
|
1.8
|
2.6
|
0.7
|
0.0
|
|
Hungary
|
-3.0
|
-4.4
|
-9.3
|
-5.9
|
-4.9
|
-4.3
|
|
Latvia
|
-2.7
|
-1.6
|
-2.7
|
-1.8
|
-2.2
|
-2.0
|
|
Lithuania
|
-2.6
|
-2.1
|
-1.4
|
-1.7
|
-2.8
|
-2.6
|
|
Malta
|
-6.5
|
-6.4
|
-5.7
|
-9.7
|
-5.9
|
-4.5
|
|
Poland
|
-1.8
|
-3.5
|
-3.6
|
-4.1
|
-6.0
|
-4.5
|
|
Czech Republic
|
-4.5
|
-6.4
|
-6.4
|
-12.9
|
-5.9
|
-5.1
|
|
Slovakia
|
-12.3
|
-6.0
|
-5.7
|
-3.6
|
-4.1
|
-3.9
|
|
Slovenia
|
-3.0
|
-2.7
|
-1.9
|
-1.8
|
-1.7
|
-1.8
|
|
New members
|
-3.2
|
-4.1
|
-4.9
|
-5.7
|
-5.0
|
-4.2
|
|
EU15
|
1.0*
|
-1.0
|
-2.0
|
-2.6
|
-2.6
|
-2.4
|
|
EU25
|
0.9*
|
-1.1
|
-2.1
|
-2.7
|
-2.7
|
-2.5
|
|
Euro zone
|
0.1*
|
-1.6
|
-2.3
|
-2.7
|
-2.7
|
-2.6
|
Applicant
States Budget Deficits
|
Applicant countries
|
2000
|
2001
|
2002
|
2003
|
2004
|
2005
|
|
Bulgaria
|
-0.5
|
0.2
|
-0.8
|
-0.1
|
-0.7
|
-1.0
|
|
Romania
|
-4.4
|
-3.5
|
-2.0
|
-2.0
|
-3.0
|
-3.0
|
|
Turkey
|
-6.1
|
-29.8
|
-12.6
|
-8.8
|
-7.1
|
-6.0
|
Member States
Government Deficits
|
New members
|
2000
|
2001
|
2002
|
2003
|
2004
|
2005
|
|
Cyprus
|
61.7
|
64.4
|
67.1
|
72.2
|
74.6
|
76.9
|
|
Estonia
|
5.0
|
4.7
|
5.7
|
5.8
|
5.4
|
5.3
|
|
Hungary
|
55.4
|
53.5
|
57.1
|
59.0
|
58.7
|
58.0
|
|
Latvia
|
13.9
|
16.2
|
15.5
|
15.6
|
16.0
|
16.1
|
|
Lithuania
|
24.3
|
23.4
|
22.8
|
21.9
|
22.8
|
23.2
|
|
Malta
|
57.1
|
61.8
|
61.7
|
72.0
|
73.9
|
75.9
|
|
Poland
|
36.6
|
36.7
|
41.2
|
45.4
|
49.1
|
50.3
|
|
Czech Republic
|
18.2
|
25.2
|
28.9
|
37.6
|
40.6
|
42.4
|
|
Slovakia
|
49.9
|
48.7
|
43.3
|
42.8
|
45.1
|
46.1
|
|
Slovenia
|
26.7
|
26.9
|
27.8
|
27.1
|
28.3
|
28.2
|
|
New members
|
36.4
|
38.5
|
39.4
|
42.2
|
44.4
|
45.2
|
|
EU15
|
64.0
|
63.2
|
62.5
|
64.0
|
64.2
|
64.2
|
|
EU25
|
62.9
|
62.1
|
61.5
|
63.1
|
63.4
|
63.4
|
|
Euro zone
|
70.4
|
69.4
|
69.2
|
70.4
|
70.9
|
70.9
|
Applicants
States – Government Deficits
|
Applicant countries
|
2000
|
2001
|
2002
|
2003
|
2004
|
2005
|
|
Bulgaria
|
73.6
|
66.2
|
53.2
|
46.2
|
44.4
|
43.2
|
|
Romania
|
23.9
|
23.2
|
23.3
|
21.8
|
23.5
|
23.5
|
|
Turkey
|
57.4
|
105.2
|
94.3
|
87.4
|
83.4
|
77.5
|
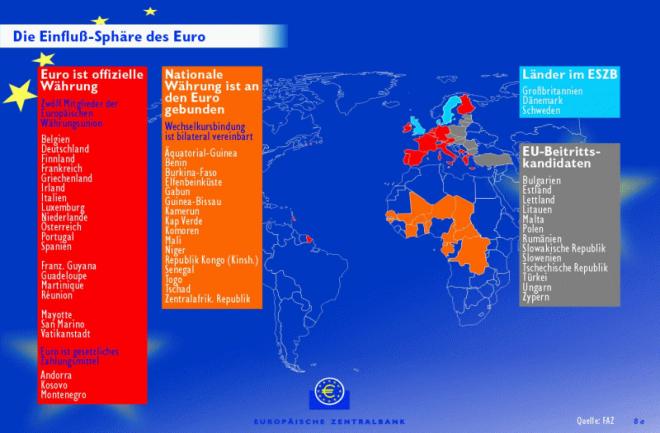
Where the Euro
can be used